面向对象的五大设计原则S.O.L.I.D,应用这些原则可以引导创建出一个更容易维护和扩展性的软件系统。
SOLID释义:
- S - Single-responsiblity Principle(单一责任原则)
- O - Open-closed Principle(开闭原则)
- L - Liskov Substitution Principle(里氏替换原则)
- I - Interface Segregation Principle(接口隔离原则)
- D - Dependency Inversion Principle(依赖倒置原则)
单一责任原则(SRP)
单一责任原则:类仅具有单一的功能
A class should have one, and only one, reason to change.
违背单一责任原则

如上是个JDK中Date的类定义,其中定义了Date format的两个方法,假设在这个基础上需要再增加另一种format方法,则需要修改类的定义类似再增加一个方法如下。
1 | public String toCustomString() { |
单一责任原则应用
1 | @deprecated As of JDK version 1.1 |
上面是方法定义上的注释已经废弃了,通过DateFormat.format(Date date)来替代format的功能。后面想扩展任何其他format格式,不用动Date本身的定义,只需要实现DateFormat接口即可以达到功能扩展。
下图是jdk中类似的思想实现,ObjectInputStream在readObjec时需要针对对象进行数据校验,校验通过定义接口ObjectInputValidation供调用方进行扩展出自定义的Validation。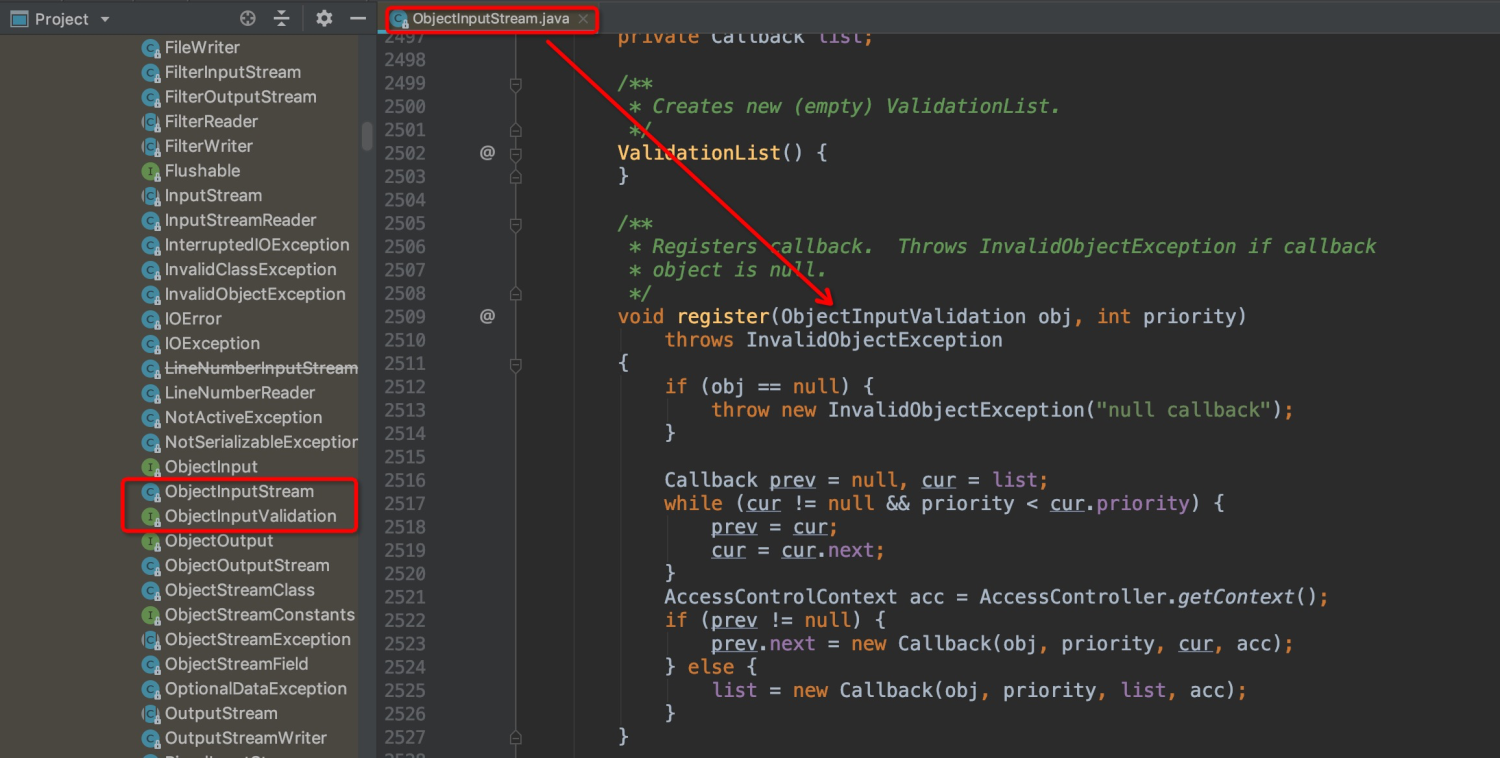
开闭原则原则(OCP)
开闭原则:软件实体应该对扩展开放对修改关闭。
Objects or entities should be open for extension but closed for modification.
违背开闭原则
1 | public List<User> sort(List<User> users, Enum type){ |
sort方法根据不同的type进行排序,随着业务发展需要增加一个用户按照体重排序,只能按照如下方式进行修改代码
1 | public List<User> sort(List<User> users, Enum type){ |
上述代码就是一个明显违背开闭原则的例子,当我们需要新增一种类型时,需要修改主流程。
开闭原则应用
按照开闭原则对上述代码进行重构,在增加新类型时不需要修改主流程,将需要修改的地方开放给到调用方。
增加体重排序逻辑只需要定义WeightComparator实现Comparator。
1 | public List<User> sort(List<User> users, Comparator<? super User> c) { |
按照体重排序的调用:sort(users, WeightComparator);
下图是JDK中类似的排序实现Arrays.sort。
里氏替换原则(LSP)
里氏替换原则:程序中的对象应该是可以在不改变程序正确性的前提下被他的子类所替换。
Let q(x) be a property provable about objects of x of type T. Then q(y) should be provable for objects y of type S where S is a subtype of T.
1 | List<String> arrays = new ArrayList<>(); |
上面是一段简单的代码,按照里氏替换原则可以被替换为如下代码。
1 | List<String> arrays = new LinkedList<>(); |
第一个替换是符合里氏替换原则没有问题,但是后两个替换不符合预期,替换后编译没有问题,但是在执行时出现运行时异常如下。
1 | java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException |
往往第一次在开发过程中遇到这个错误会很诧异,为什么会抛出来异常信息,他不是一个List吗?是不是jdk中的包也有不符合里氏替换原则的,严格意义上来说是的。但是我们去看一下List
1 | /** |
他在方法注释上声明了,如果List不支持add操作会抛出UnsupportedOperationException。虽然List
接口隔离原则(ISP)
接口隔离原则:子类中不应该被迫依赖于他们不使用的方法
clients should not be forced to implement the unwanted methods of an interface
违反接口隔离原则
1 | public interface MediaPlayer { |
1 | public class VlcMediaPlayer implements MediaPlayer { |
1 | public class WinampMediaPlayer implements MediaPlayer { |
WinampMediaPlayer不支持playVideo方法,但是其实现了MediaPlayer所以也被迫实现了playVideo方法。
接口隔离原则应用
1 | public interface AudioMediaPlayer { |
1 | public interface VideoMediaPlayer { |
将MediaPlayer接口中的方法按照功能拆分出AudioMediaPlayer、VideoMediaPlayer,只有音频播放能力的播放器只需要实现AudioMediaPlayer。
1 | public class VlcMediaPlayer implements VideoMediaPlayer, AudioMediaPlayer { |
1 | public class WinampMediaPlayer implements AudioMediaPlayer { |
WinampMediaPlayer实现接口AudioMediaPlayer,避免被迫实现playVideo方法。
下图JDK中的双向链表,实现List、Deque两个接口。
依赖倒置原则(DIP)
依赖倒置原则:高层模块不应该依赖低层模块,两者都应该依赖抽象;抽象不应该依赖细节,细节应该依赖抽象。
High level modules shouldnot depend upon low level modules.Both should depend upon abstractions. Abstractions should not depend upon details. Details should depend upon abstractions

图中是人去拿起水杯喝水,逻辑上是人依赖于水杯的实现,但是再思考一下,人的手型是确定的,其实是我们在生产水杯的时候适配人的手型去生产的。
总结
S.O.L.I.D面向对象的设计,能够指导我们去更好的构建容易维护、扩展性搞的系统,几种原则需要反复结合日常开发过程中的一些思考不断强化,逐步理解到运用。
参考资料
SOLID: The First 5 Principles of Object Oriented Design